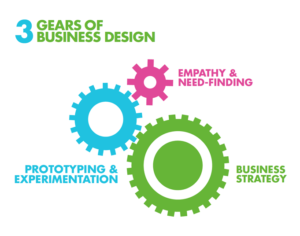
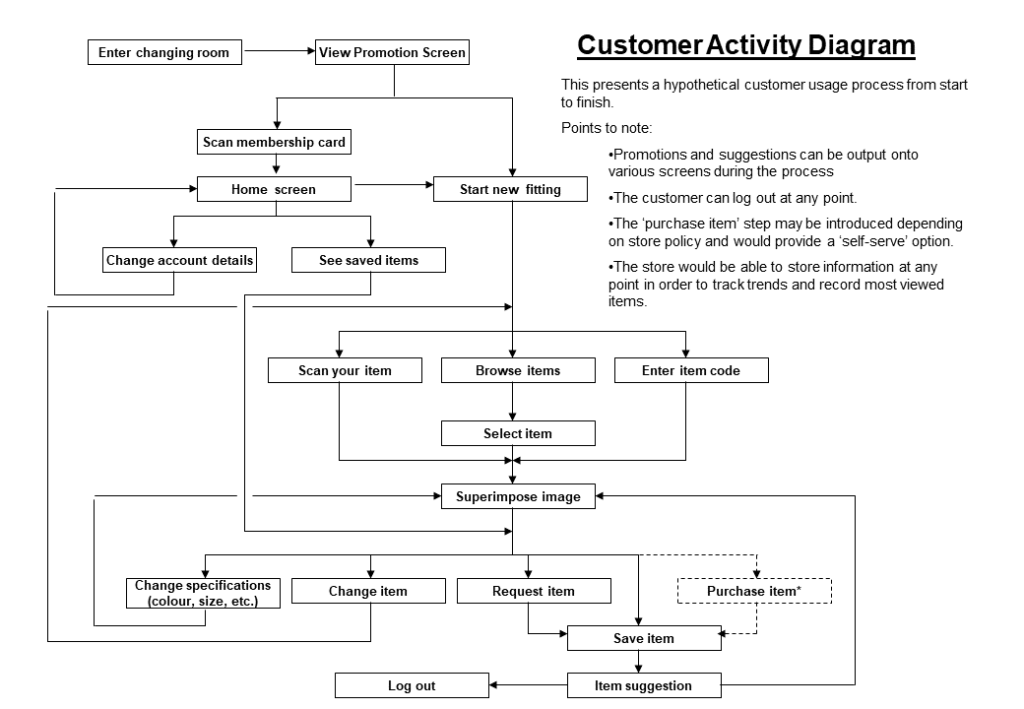
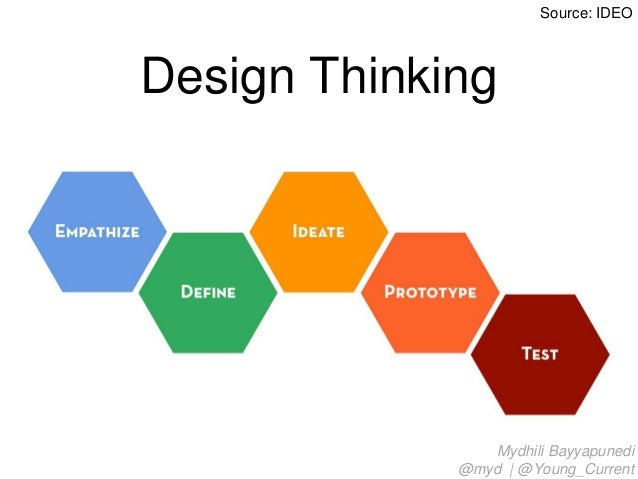
Business Design is an emerging commercial discipline. The best definition of business design that I have seen comes from IDEO, the company that first introduced me to the concept:
“Business designers take juicy, creative, human-centered innovation and make it succeed out there in the real world. We [IDEO] use strategy, analysis, and financial modeling as generative design tools, and help organizations turn their biggest, wildest ideas into businesses with long-term viability.”
The Rotman School of Business at the University of Toronto defines it as follows:
“Business Design is a human-centred approach to innovation. It applies the principles and practices of design to help organizations create new value and new forms of competitive advantage. At its core, Business Design is the integration of customer empathy, experience design and business strategy.“
What does a Business Designer do?
During a discussion with Lorenz Koder Fort at IDEO, I learned that the key activities of a business designer are:
- understanding the business and the competition
- providing industry perspectives
- designing experiments for prototyping
- measuring the results of those experiments
- identifying risks and mitigating strategies
- identifying differentiation strategies
- developing business models/cases with financial models to support investment
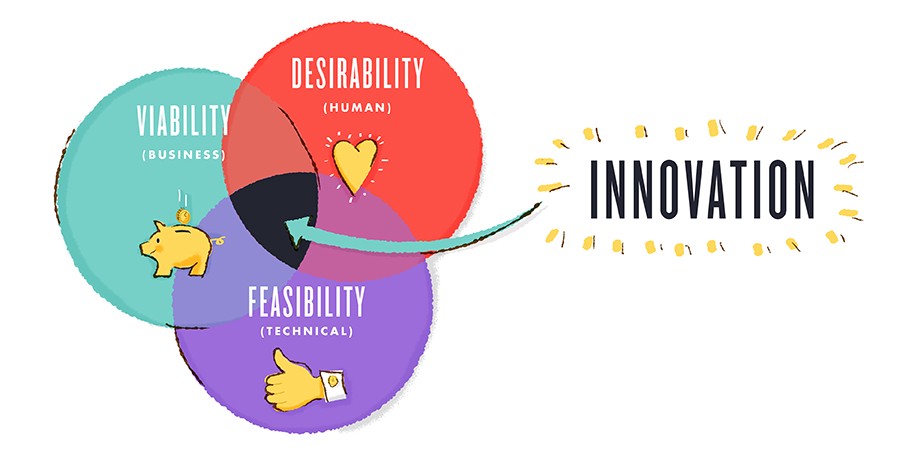
In particular, he intimated that Business Designers are focussed on the Viability segment of the Feasibility, Viability, Desirability nexus (diagram above). As such, IDEO assesses potential Business Designers along 4 core pillars within that:
- Market Navigation
- Prototyping & Offer Design
- Business Modelling
- Storytelling
There’s also a great summary of the typical work of a Business Designer given in the LinkedIn bio of Alvaro Rojo, Business Design Lead at Fjord:
- Disruptive trends & competitive forces
- Discovery-driven planning
- Customer experience strategy
- Value proposition design
- New product/service development & execution
- Market size & growth
- Ecosystem mapping
- Roadmapping
- Go-to-market strategy & international expansion
- KPIs modeling & tracking
- MVP & in-market prototyping
- Product/market fit optimization
- Business model design & monetization opportunities
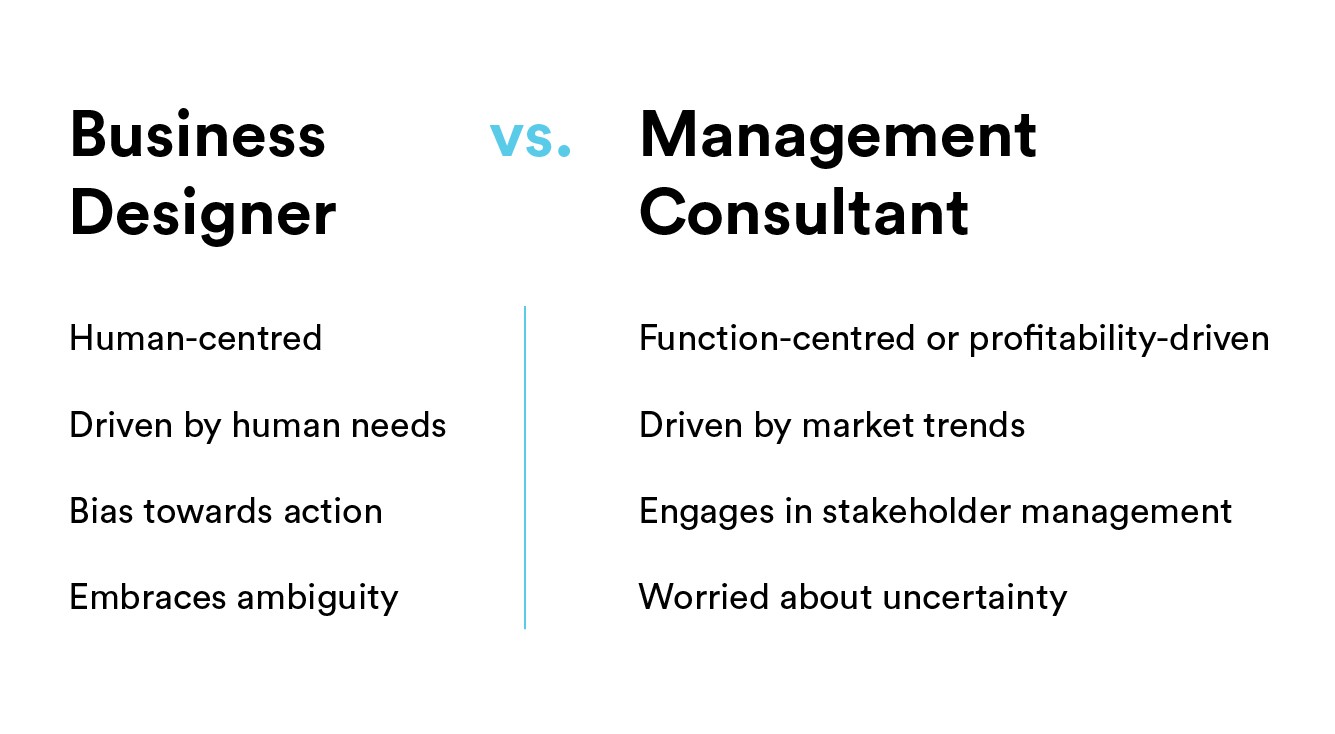
Finally, Tsukasa Tanimoto’s informative Medium post contains this succint explanation of the difference between a Business Designer and a Management Consultant:
Who offers Business Design services to their clients?
Many companies offer Business Design-type services to their clients, but here is a selection of some interesting companies in this space:
- IDEO
- Fjord (owned by Accenture)
- EY-Seren (owned by EY)
- MAYA Design (owned by BCG)
- PA Consulting
- frog design
- SYPartners
- Fahrenheit 212
- ?What If! Innovation
How can I learn Business Design?
You can study an MBA with a major in Business Design at the Rotman School of Management at the University of Toronto.
The Stanford Hasso Plattner Institute of Design, or “the d.school“, seems to be a renowned institution for the discipline. This makes sense, as David Kelley, one of IDEO’s founders, founded the d.school as well!
IDEO offers a lot of related short courses through their IDEO U website, but Designing a Business hits the nail on the head!
How can I become a Business Designer?
A lot of job ads state that MBAs are a “huge plus”, but in reality, it seems to me that they are pretty much a pre-requisite. In some ways, this makes sense, as a holistic view of a business is crucial to designing a good one! However, it does exclude the autodidacts among us.
Entrepreneurship experience is highly valued, as entrepreneurs have lived and breathed the design, prototype, and test cycle.
There’s further discussion of the role and what companies are looking for in a potential recruit on this post from an ex-IDEO Business Designer and the previously mentioned in-depth post from Tsukasa Tanimoto, a Service & Business Designer at Spotless.